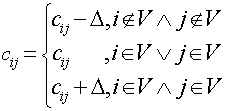Hungarian Algorithm
- views: 0
- author: ha4219
- August 01, 2022
- 4 min read
Hungarian Algorithm
아래 글 참조
Problem Statement
가장 대표적으로 명의 사람에게 개의 일을 담당하는 문제를 생각해보자. 각 사람은 1개의 일을 담당할 수 있으며 이에 대한 가 발생한다. 그러면 기업 입장에서 목표는 이 비용을 최소화하며 개의 일을 배치해야 한다.
아래는 위 설명을 식으로 설명한 것이다.
: cost matrix, where : cost of to perform job .
: resulting binary matrix, where if and only if worker is assigned to job.
, : one worker to one job assignment.
, : one job to one worker assignment.
: total cost function.
우리는 이 문제를 그래프 문제로 바꿔 생각할 수 있다. 명의 사람에게 개의 일에 대한 가 주어졌다고 생각하면 각 명의 사람에게 개의 일이 간선으로 연결되어 있어 총 개의 간선이 연결된 그래프로 표현할 수 있다. 아래 예시를 보자.
General Description Of The Algorithm
이러한 문제를 할당문제라고 한다.
이 문제를 foolish하게 해결하면 이면 해결 할 수 있다. bfs, dfs로 순열을 찾고 이에 대한 cost를 계산해 최소값을 찾는다.
쉽게 할 수 있지만 문제를 해결하기에 적합한 시간복잡도는 아니다.
효율적인 방법의 알고리즘을 보여줄 텐데 하나는 쉽고 빠르게 이고 다른 하나는 구현이 복잡하지만 이다.
Algorithm Explanation
이분 그래프로 이 문제를 다루겠다.
Step 0)
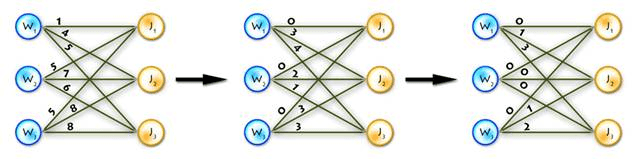
- For each vertex from left part(workers) find the minimal outgoing edge and subtract its weight from all weights connected with this vertex. This will introduce 0-weight edges (at least one).
- Apply the same procedure for the vertices in the right part (jobs).
실제 이 순서는 필요하지 않지만 main cycle 수를 줄일 수 있다.
Step 1)
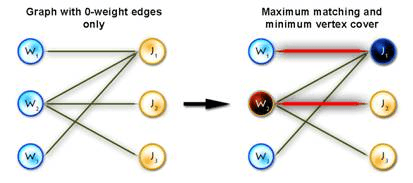
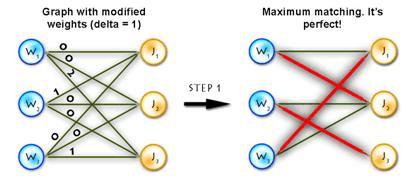
- Find the maximum matching using only 0-weight edges (for this purpose you can use max-flow algorithm, augmenting path algorithm, etc.).
- If it is perfect, then the problem is solved. Otherwise find the minimum vertex cover (for the subgraph with 0-weight edges only), the best way to do this is to use Köning’s graph theorem.
Step 2)
Let and adjust the weights using the following rule:
Step 3)
Repeat Step 1 until solved.
But there is a nuance here; finding the maximum matching in step 1 on each iteration will cause the algorithm to become . In order to avoid this, on each step we can just modify the matching from the previous step, which only takes operations.
It’s easy to see that no more than iterations will occur, because every time at least one edge becomes 0-weight. Therefore, the overall complexity is